To refrain from using or significantly reduce the intake of tobacco and alcoholic beverages
Route to Parenthood
Men with fertility disorders should not lose their hope to conceive a child as medicine can suggest several solutions to such problems. This chapter is dedicated to reviewing the main methods of treatment of male infertility and artificial insemination, the reasons why the sperm DNA plays such a huge role in artificial insemination and the means to protect sperm DNA from oxidative stress.
Treatment of Male Infertility
with Known Causes
Treatment of erectile dysfunction and disorders of ejaculation
Erectile dysfunction and disorders of ejaculation are usually treated by prescribing medication that improves erection or ejaculation. Electro-stimulation can also be used to treat disorders of ejaculation. If neither of these methods yields any results, the patient is recommended to undergo TESA-ICSI. These and all other artificial insemination procedures are discussed in the chapter titled ART (Assisted Reproduction Technologies).
Hypogonadism
Hypogonadism is hormonal imbalance in the male body (lack of testosterone, luteinizing hormone or follicle-stimulating hormone). Such disorders are usually managed by prescribing hormone therapy or by recommending artificial insemination.
Obstruction
The general approach towards treatment of infertility caused by obstruction is a microsurgery, if such is possible. The urogenital ducts are spread and opened up during the surgery via mechanical means.
Varicocele
Varicocele accounts for almost every sixth case of male infertility. Varicose vein processes impede blood circulation in the testicles, resulting in lower supply of oxygen and nutrients required for spermatogenesis along with metabolite elimination failure. In turn, this leads to increased vascular permeability due to which fluids start accumulating in the testicles and inflammation processes begin. The subsequent oxidative stress damages sperm DNA and is the key reason behind deteriorated sperm quality parameters.
No unanimous opinion regarding the treatment of varicocele exists so far. The surgical treatment of varicocele is also still under debate. The European Association of Urology indicates that such method of treatment is only effective in adolescence when varicose vein processes impede the development of testicles.
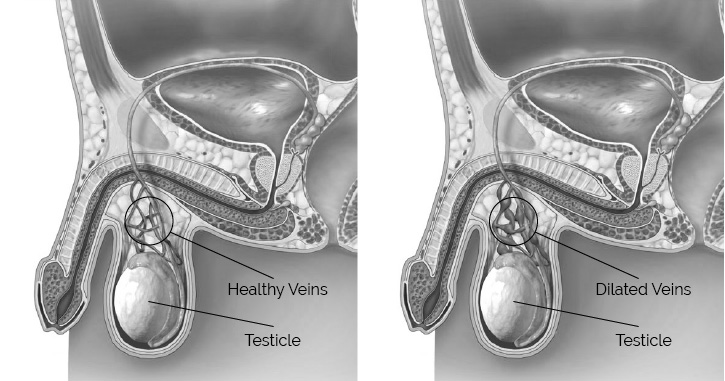
As referenced previously, surgical treatment of varicocele may take two forms: vein ligation and stripping or sclerotherapy. The traditional vein ligation and stripping employs the open surgery approach while sclerotherapy is performed via laparoscopy. However, if the surgical treatment is deemed ineffective and the sperm quality remains low, the patient is recommended to undergo ART (IVF, ICSI).
Treatment of idiopathic male infertility (infertility of unascertained cause)
Almost every third man facing fertility issues is diagnosed with idiopathic male infertility, i.e. infertility of unascertained cause. As stated in earlier chapter, idiopathic male infertility is diagnosed when all other clear medical causes are rejected. However, oxidative stress is presumed to be the underlying reason behind idiopathic male infertility. Oxidative stress is caused by “smoldering” inflammations, polluted environment, stress and certain other diseases.
As a rule, medication-based treatment of idiopathic male infertility is practically ineffective; hence, upon such diagnosis, the couple is usually referred to a specialist of ART. Along with ART procedures, the men are recommended to start a healthy lifestyle and take antioxidants.
The discussion of possible ways to treat male infertility shows that in most cases, i.e. upon diagnosis of idiopathic male infertility, varicocele or obstructive azoospermia, ART is the recommended route. The same practice is applied when medication-based or surgical treatment proves unsuccessful or the female partner is also found to have fertility-related disorders, e.g., ovulatory disorders or in most cases, polycystic ovary syndrome.
ART (Assisted Reproduction Technologies)
- OVULATION INDUCTION involves the use of medication to stimulate development of one or more mature follicles (where eggs develop) in the ovaries of woman who have anovulation and infertility. These women do not regularly develop mature follicles without help from ovulation enhancing drugs.
- IUI (intrauterine insemination) is a less frequently used method of artificial insemination during which a sperm collected and prepared via special means is placed into uterus with a specific-purpose catheter. This method is very close to natural insemination means and is most often employed when the sperm is subfertile (decreased fertility but spermatozoa are capable of fertilizing the egg cell), i.e. the sperm count is less than 20 million/ml and their progressive motility is below 50% (based on the nominal values published by WHO). IUI requires for the sperm DNA to be unbroken and for the spermatozoa to retain their normal form and sufficient motility. IUI may be performed by stimulating the ovulation, e.g. via the follicle-stimulating hormone-releasing factor, or takes place in a natural cycle.
- IVF (in vitro fertilization) is a type of ART during which the ovum is fertilized by a sperm outside the woman’s body, i.e. in a dish or test tube; thus, the name in vitro (in glass). During the course of the procedure, special medications are used to stimulate the ovaries to produce more egg cells which are then taken from the woman’s body via special means. Then, a specifically processed sperm is placed in a dish next to the selected ovum, and the fertilization process takes place. Fertilized eggs are kept in incubators under special conditions until they grow into embryos. Later, a certain number of embryos are transferred to the uterus and the couple waits for the woman to get pregnant.IVF is a rather widely used method, especially when a male partner is diagnosed with idiopathic infertility (and either medication-based or surgical treatment bears no results). IVF is also a suitable choice when sperm quality is excessively low or prior treatment using other methods has proven to be unsuccessful.
- ICSI (introcystoplastic sperm injection) is a procedure of ART which is very similar to IVF in nature. The only difference lies in the fact that during the IVF, the semen is specifically “prepared” to hold many spermatozoa, while the ICSI method involves the injection of a single spermatozoon received via testicle puncture (TESA). The ICSI is performed with the help of a microscope: one egg and one sperm are taken and the sperm is injected into the egg by puncturing it with a very fine needle. The following steps coincide with those of the IVF procedure.ICSI is mostly employed when the sperm quality is excessively low or the ejaculate contains no sperm whatsoever, and also in cases of severe immune infertility or unsuccessful IVF.
„DNA integrity of spermatozoa is especially important for the success
of IVF and ICSI.“
The practice of ART has its own drawbacks. For one, the women have to undergo many unpleasant procedures such as hormonal stimulation which may have highly severe consequences (e.g., ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome that may endanger the woman’s life) and egg retrieval from the ovaries with a 30-40 cm long needle. The men also have to suffer though several less than desirable procedures, e.g., TESA (testicular sperm aspiration).
Apart from the discomfort felt during the treatment, financial status is yet another important factor as the cost of artificial insemination is quite high. In addition to that, no one can guarantee that the first time will be successful and a child will be conceived. The fertility clinics in the Western world have published data showing that the probability of the first ART to be successful is as many as 40%. The rate of success in conceiving a child increases to 60% upon the fourth procedure of ART.
DNA Protection from Damage

As discussed before, it is most important for the sperm DNA to be undamaged and well protected if one wishes to have children in the future. Hence, it might be of some benefit to know of ways how to contribute to this goal with maximum effort.
The previous chapters detailed how free radicals formed in cases of idiopathic infertility, varicocele, infections, etc. Our body has a type of natural protection in the form of antioxidants which neutralize the free radicals. Antioxidants can be categorized under three main defense mechanisms: enzymatic, non-enzymatic and by reducing activity of matrix metalloproteinases.
“Every man encountering fertility problems can raise his
probability of having children without any complex
medical procedures.”
The enzymatic antioxidant is the key and most effective mechanism of defense neutralizing free radicals. This mechanism is comprised of several groups of enzymes such as glutathione peroxidase or superoxide dismutase. These enzymes have a protein structure and a composition containing certain metals (selenium, zinc). The glutathione peroxidase enzyme utilizes reduced glutathione to react with a free radical and neutralize it transforming the molecule into a harmless one, e.g. a water molecule. Then, the glutathione reductase enzyme reacts as well causing the entire mechanism to be “restored” and ready to neutralize other free radicals.
The enzymatic antioxidant defense mechanism plays a huge role in spermatogenesis (sperm production) due to the following two reasons:
- It neutralizes free radicals. The process of spermatogenesis is a very intense one and produces large quantities of free radicals. If not neutralized, the formed free radicals may damage both the spermatozoa and their DNA. It neutralizes free radicals. The process of spermatogenesis is a very intense one and produces large quantities of free radicals. If not neutralized, the formed free radicals may damage both the spermatozoa and their DNA.
- In case of varicocele, blood circulation in the testicles slows down, the supply of nutrients deteriorates and certain substances are released actively producing free radicals.
Important facts on enzymatic antioxidant defense:
- Deficiency of selenium or zinc may negatively affect the enzymatic antioxidant defense.
- The enzymatic antioxidant defense is unique because unlike the non-enzymatic one, it is self-restoring.
- Yet another exceptional quality of the enzymatic antioxidant defense mechanism is that it starts working only when the quantity of free radicals in the body increases.
Non-enzymatic antioxidant defense mechanism is a much simpler one. It is comprised of antioxidant vitamins C, E, B6, B12, folic acid, L-carnitine, lycopene and/or similar substances that chemically bind the free radicals.
Metalloproteinases are enzymes capable to degrade all kinds of extracellular matrix proteins. Metalloproteinases may increase oxidative stress and in such a way induce apoptosis of spermatozoons. Scientific researches have shown that substances such as Coenzyme Q10, Selenium and Glutathione decrease activity of metalloproteinases.
The antioxidants are highly important when the spermatozoa flow along the urogenital ducts because:
- When immature sperm cells travel along the mature spermatozoa, the former release a rather large number of free radicals that damage the normal shaped mature sperm. Studies have shown that the antioxidants present in the semen protect the mature sperm from the free radicals. When immature sperm cells travel along the mature spermatozoa, the former release a rather large number of free radicals that damage the normal shaped mature sperm. Studies have shown that the antioxidants present in the semen protect the mature sperm from the free radicals.
- Another factor in play during the sperm travel through the urogenital ducts is the constant “smoldering” inflammation. Almost every third infertile man suffers from asymptomatic inflammation; hence, it is important to ensure that all inflammation foci are completely eliminated to protect the spermatozoa.
Ensuring smooth running of the enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidant defense mechanisms and reducing inflammatory processes in the urogenital ducts lead to less fractured sperm DNA, superior sperm quality and, consequently, higher probability of having children.